Formaldehyde is invisible, which can be perceived only by smell. Under the guideline value issued by the Ministry of Health Labor and Welfare of Japan which is 100μg/㎥(0.08ppm)could be hardly recognized. However, living in that situation continually would increase the risk of cancer. That makes the measures and prevention of formaldehyde in advance, likes other virus, are so important.

Estimated maximum life time (0〜70 years old) risk of cancer for people exposed daily in their lives, which is:
Pharyngeal cancer: 0.011ppm lymphoma cancer: 0.017ppm Leukemia: 0.057ppm;
The incidence of carcinogenic caused by formaldehyde of
general adult
0.08ppm:100μg(according to the statistics of guideline value issued by Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan, indoor temperature at 23℃ )which is 1 in 100;
0.04ppm:50μg (according to the statistics of guideline value issued by Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan, indoor temperature at 23℃ )which is 1 in 250;
The risk to infants under 2 years old is 1 in 10 people, that is 10 times of adult, and those young men under 16 are 3 times of adult.
Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan has established the guideline value of formaldehyde in the indoor environment which is 100μg/㎥(0.08ppm) as measures for sick house syndrome. The use of building materials dissipating formaldehyde has been restricted by the Building Standards Law. In the specialized agencies of the worlds, such as the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), the lower agency of the World Health Organization (WHO), classified formaldehyde as a carcinogen in Group 1 (observed as chemical carcinogen to human)of carcinogens list, the same as arsenic, asbestos, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, and plutonium. In Japan, as carcinogen, it has been listed in the 2nd Group A in Japan Society Occupational Health. Such recognition as a carcinogen is growing. However, we can’t deny that the correspondence is still insufficient.

In our living environment and inhabited, many objects contains formaldehyde.
 Clothing
Clothing furniture
furniture Wallpaper
Wallpaper Curtain
Curtain Car
Car Cigarette
Cigarette Toy
Toy Stuffed Toy
Stuffed ToyInterior material of the automobile also dissipate formaldehyde and other chemicals, which is the cause of mental instability and poor physical condition, the same as sick house syndrome, it is called sick car syndrome. It is quite dangerous if it happens during the driving, that could lead to an accident. The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) listed the car internal air pollution as one of the five risk of major environmental pollution.
Adhesives or plasticizers, resins, plastics, residual chemicals used in the car manufacturing process and smoking will dissipate formaldehyde. Among them, during the manufacturing procedure of the interior materials of automobile, synthetic resins like phenol resin or melamine resin are being used as raw materials to react with formaldehyde. However, formaldehyde remains in the resin because of incomplete reaction with the raw materials, which will be dissipated later.
In the web site of JAMA (Japan Automobile Manufacturers Association), there is a report about the change of formaldehyde over time and temperature after the manufacturing of automobile. According to the report, we can see that 40% of the existing concentration of formaldehyde are continued to dissipate even after over one year of manufacture. In addition, according to the report of temperature dependence, we can see that when the room temperature is 35℃, 200% of the exiting concentration of formaldehyde is filled in the car.
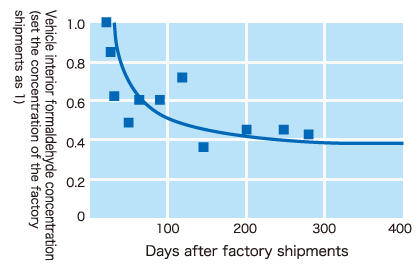
Generally, the concentration of formaldehyde in the car will decrease continually over time. But after one year the emission rate will be maintained about 40%, and it will continue to dissipate over a long period of time thereafter.
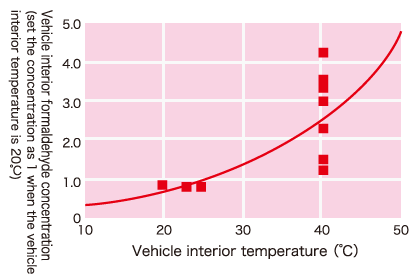
The concentration of formaldehyde in the car will be rise along with the rising temperature. It could be rise to 3 to 4 times when the car parking under the scorching sun.
Formaldehyde concentration would be change by the temperature. It is necessary to calculate the temperature in「Ct=Ct2×1.09(t-t2)」. That means when the room temperature rise 1℃ each time, it is necessary to multiply the temperature difference factor by the coefficient of 1.09.
In fact, we verified it by measuring the concentration of formaldehyde in a mansion in winter.


The above data is lower than the guideline value. The temperature was 17℃ that day, the data will change according with the rising temperature. For example, when the room temperature rise at 25℃, the result of the formaldehyde concentration calculation by the formula is as followed:

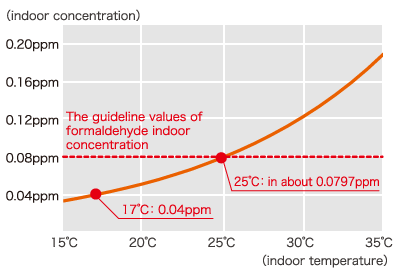
※ As described above, even the concentration of formaldehyde is about half of the guideline value, when the room temperature rise at 25℃, it will also rise close to the standard value. It is possible that the concentration will exceed the guideline value if the ventilation is insufficient, or other formaldehyde emission elements are increased, such as new arrangement of furniture, etc.

The value is lowered as the limit value. Even when the temperature rises, the value will be greatly lower than the guideline concentration value.
※“Formaldehyde detection tube 710”by KOMYO RIKAGAKU KOGYO K.K. The value was lower than the detection limit, so wrote as under 0.01ppm.
